Solar panels are the heart of any clean energy system, converting sunlight into power for your home or business. But have you ever wondered: how far can solar panels be from the inverter or battery before efficiency takes a hit? And why does the spacing between panels and your roof matter? These questions often go unanswered in basic installation guides. This article dives into the technical details of solar panel distance and roof spacing, revealing hidden factors like cable resistance, voltage drop, and heat management. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a solar pro, these insights will help you optimize your system for peak performance.
The Maximum Effective Distance Between Solar Panels and Inverter/Battery
One of the most critical aspects of solar installation is the distance between your solar panels and the inverter or battery. Too far, and you could lose power due to cable resistance and voltage drop. Let’s break it down.
Cable Resistance and Voltage Drop
The efficiency of your solar system depends on how well electricity travels from panels to the inverter or battery. Voltage drop occurs when current flows through a cable, losing energy due to resistance. The formula is simple: Vdrop = I × R (current × resistance). For example, a typical AWG 10 copper cable has a resistance of about 1 ohm per 1000 feet. With a 300W panel producing 10 amps at 30 volts, a 100-foot cable run could result in a 1-volt drop—roughly a 3.3% efficiency loss. Industry standards recommend keeping voltage drop below 2-3%, meaning the maximum effective distance is often 50-100 feet, depending on your setup.
Real-World Scenarios
- Small Home System (3kW): With a lower current (around 10-15A), a distance of under 50 feet is ideal to minimize losses.
- Larger System (10kW): Higher currents (up to 40A) require thicker cables (e.g., AWG 8) or series connections to boost voltage (e.g., from 24V to 48V), allowing distances up to 100 feet or more.
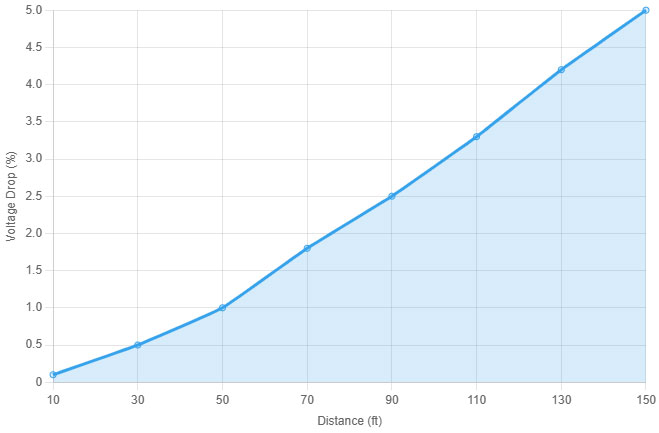
To visualize this, consider the following data: a 10-foot run might lose 0.1% efficiency, while a 150-foot run could lose 5% or more, rendering the system less cost-effective.
Authoritative Insight: For a deeper understanding of electrical resistance in solar systems, check out the principles outlined on Wikipedia’s page on electrical resistance.
The Role of Roof Spacing: Cooling, Cleaning, and Structural Safety
Spacing between solar panels and the roof isn’t just about aesthetics—it’s a technical necessity. Proper gap design enhances performance and longevity. Here’s why.
Cooling
Solar panels operate best at lower temperatures. For every 1°C rise above 25°C, efficiency drops by about 0.5%. A 4-6 inch (10-15 cm) gap allows air to circulate, reducing heat buildup. In hot climates, this can prevent efficiency losses of up to 10-15% during peak summer months.
Cleaning
Dust, leaves, and bird droppings can reduce panel output by 20% if left unchecked. Adequate spacing makes it easier to clean panels with a soft brush or hose, maintaining optimal performance. Without this, you might need professional cleaning every few months, adding costs.
Structural Safety
Roofs expand and contract with temperature changes. A small gap reduces stress on mounting hardware and prevents long-term damage. The U.S. National Electrical Code (NEC) recommends minimum spacing to ensure safety and compliance, a standard echoed by many global building codes.
Optimization Tips: Reducing Line Losses and Boosting Efficiency
Maximizing your solar system’s efficiency requires smart layout decisions. Here are actionable steps:
Shorten the Distance
Place the inverter or battery as close as possible to the panels. For instance, mounting a microinverter directly beneath each panel can cut cable runs to under 10 feet, minimizing losses.
Choose the Right Cable
Thicker cables (e.g., AWG 8 instead of AWG 10) have lower resistance. For a 100-foot run with 20A current, upgrading to AWG 8 can reduce voltage drop from 2% to 1%, saving energy.
Increase Voltage
Connecting panels in series raises system voltage (e.g., from 24V to 48V), reducing current and line losses. This is especially useful for larger installations spanning long distances.
Monitor Performance
Invest in a system with real-time monitoring, like those paired with high-quality lithium battery packs. For a reliable option, check out Docan Tech’s lithium battery pack, designed to optimize energy storage and efficiency.
Conclusion: Unlock Your Solar System’s Full Potential
The distance between your solar panels and inverter/battery, along with proper roof spacing, plays a pivotal role in system efficiency. By keeping cable runs short, choosing the right materials, and ensuring adequate ventilation, you can minimize losses and maximize output. Start optimizing your layout today with these tips, and explore more resources on Wikipedia’s solar energy page for advanced insights.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How far can solar panels be from the inverter before efficiency drops?
Efficiency starts declining beyond 50-100 feet due to voltage drop. Keep it under 50 feet for small systems or use thicker cables for longer runs.
What happens if roof spacing is too small?
Insufficient spacing traps heat, reducing efficiency by up to 15%, and makes cleaning difficult, leading to further losses.
How do I choose cables to reduce voltage drop?
Use AWG 8 or thicker cables for distances over 50 feet, and calculate voltage drop using Vdrop = I × R to stay within 2-3%.
How much does panel spacing affect cooling?
A 4-6 inch gap can lower panel temperature by 10-20°C, boosting efficiency by 5-10% in hot conditions.
Can distance affect my battery’s lifespan?
Yes, excessive voltage drop can undercharge batteries, reducing their lifespan. Optimal distance and cable choice are key.


Leave a Comment